Shaping the Future: The Role of 3D Printing and Injection Molding in Automotive Manufacturing
Share
Share
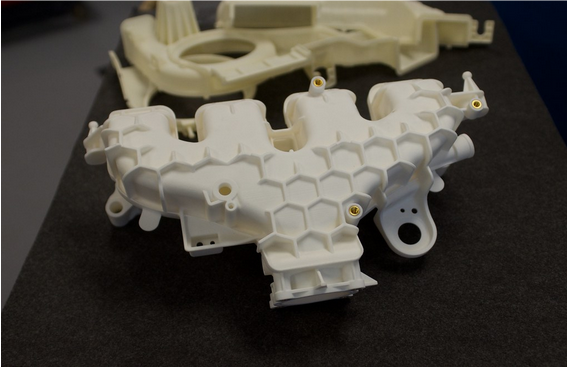
The automotive industry stands on the brink of a revolution, with two distinct manufacturing technologies at its core: 3D printing and injection molding. This comprehensive exploration delves into each method’s intricacies, evaluates their capabilities in creating complex auto parts, and anticipates the future of automotive manufacturing.
In the vast and intricate world of automotive manufacturing, two technologies have emerged as pivotal in shaping the future: 3D printing and injection molding. Each offers unique advantages and has significantly influenced how auto parts are designed, developed, and produced. This section provides a glimpse into their significance within the auto industry, underscored by a comparative table that highlights their key differences.
3D printing, a marvel of modern engineering, brings digital designs to life through a layer-by-layer construction process. This technology has been a game-changer in various industries, particularly in automotive manufacturing, where precision, efficiency, and innovation are paramount. The essence of 3D printing lies in its versatility and the myriad of technologies it encompasses, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), each suitable for different applications in automotive parts manufacturing.
Injection molding, on the other hand, is a time-honored process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create custom injection molded parts with high precision and consistency. This method is renowned for its ability to produce high volumes of parts with excellent material properties, making it a staple in automotive manufacturing. Common materials used in this process include:
3D printing’s layer-by-layer approach affords unparalleled design flexibility, enabling the creation of parts that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability opens up new vistas in automotive design, from intricate lightweight structures to complex geometries that optimize performance while reducing material waste.
While injection molding is limited by the need for mold creation for each new material, 3D printing thrives on material diversity, capable of handling a vast array of materials – from plastics and metals to composite blends. This diversity not only enhances part complexity but also allows for unprecedented levels of customization and innovation.
For small-batch productions or highly specialized components, 3D printing is the more economical choice, eliminating the need for expensive molds and allowing for quick iterations at a minimal cost.
 Rapid Prototyping and Innovation
Rapid Prototyping and Innovation3D printing accelerates the design process, enabling rapid prototyping and testing, thus fostering innovation and allowing automotive manufacturers to bring new concepts to market faster than ever before.
When it comes to mass production, injection molding reigns supreme, offering unmatched speed and efficiency, making it ideal for high-volume automotive part production.
Injection molding ensures consistent part quality and superior material properties, crucial for components that must meet stringent automotive standards.
Innovative automotive parts such as intricate cooling systems, lightweight structural components, and complex engine parts exemplify 3D printing’s potential. These case studies not only highlight the technology’s versatility but also its capability to push the boundaries of automotive design and functionality.
 Hybrid Manufacturing Processes
Hybrid Manufacturing ProcessesThe integration of 3D printing and injection molding holds immense potential, combining the best of both worlds to achieve optimal manufacturing outcomes. This hybrid approach enables manufacturers to leverage 3D printing for design flexibility and injection molding for production efficiency.
Advancements in materials science are set to further blur the lines between 3D printing and injection molding, with new materials offering the benefits of both methods. This progress promises to significantly impact the choice between these technologies, offering more versatile solutions for automotive parts manufacturing.
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends on various factors, including production volume, part complexity, material requirements, and cost considerations. For instance, 3D printing is the preferred choice for low-volume production of complex parts, allowing for greater design flexibility and rapid prototyping. Injection molding, however, is unmatched in its ability to efficiently produce high volumes of parts with consistent quality and strength.
A decision-making flowchart can aid in this process, guiding manufacturers through a series of questions about their project’s specific needs to determine the most suitable manufacturing method.
 Addressing the Limitations of 3D Printing
Addressing the Limitations of 3D PrintingWhile 3D printing offers remarkable design flexibility, it faces challenges such as speed and size constraints for larger production runs. However, ongoing advancements in 3D printing technology are steadily overcoming these hurdles, enhancing its viability for a broader range of automotive manufacturing applications.
Injection molding’s main drawbacks include the high initial costs associated with mold design and fabrication, and its limited ability to accommodate complex geometries without increasing costs significantly. Additionally, the environmental impact of waste material from the injection molding process is a growing concern. Efforts to make injection molding more sustainable include recycling programs and the development of eco-friendly materials.
The automotive industry’s future is intricately linked to the evolution of manufacturing technologies like 3D printing and injection molding. Each has its unique strengths and limitations, but together, they offer a comprehensive range of solutions for automotive parts manufacturing. As these technologies continue to advance, their integration promises to unlock new levels of efficiency, innovation, and sustainability. Looking forward, the key to harnessing their full potential lies in understanding their capabilities, making informed choices based on specific project requirements, and staying abreast of ongoing technological advancements.
The journey through the complexities of 3D printing and injection molding in automotive manufacturing reveals a landscape rich with opportunities for innovation, customization, and improved efficiency. As the industry moves forward, integrating these technologies is a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence in automotive manufacturing, driving us toward a future where the possibilities are as limitless as the roads that stretch before us.
Leave a Reply